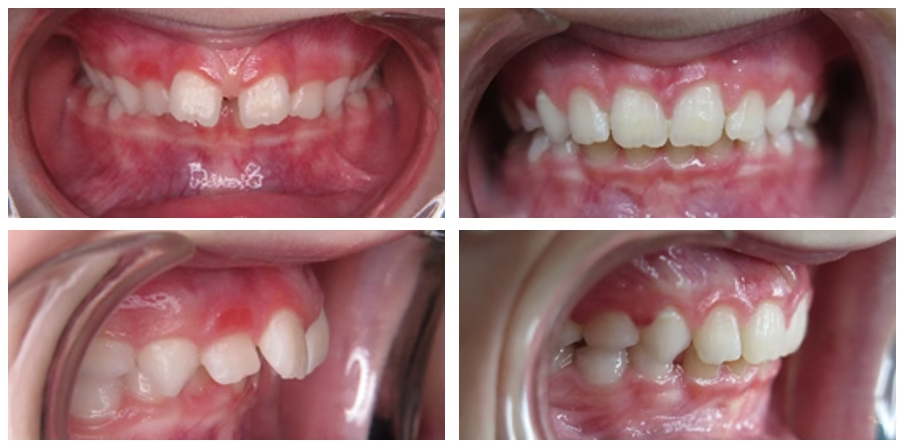
Myofunctional therapy
Crooked teeth and developmental problems of the jaws can become worse as the adult teeth/face develop. Habits such as mouth breathing and incorrect lip and tongue function ( tongue thrusting, grinding behavior, incorrect swallowing pattern and thumb sucking) are the biggest causes of crooked teeth and incorrect jaw development. If these habits persist into adulthood, it may result in the need for complex orthodontic treatment. It is best to adjust these habits first, to avoid the chance of relapse after orthodontics.
By addressing abnormal oral habits at a young age, teeth and jaws develop optimally, overall health improves and the need for braces is significantly reduced!
We do this with the help of Oro Myo Functional Therapy in combination with the Myobrace. This is a preventive pre-orthodontic treatment that focuses on the underlying causes of crooked teeth. Oromyofunctional therapy can be started at different ages. In our practice we generally treat 7/8 year olds. So often before orthodontics could even be used.
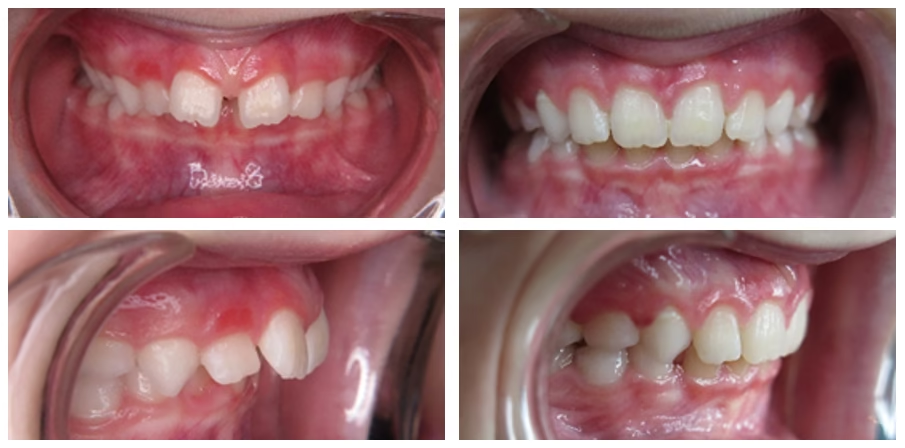
Myobrace
A Myobrace is also called a muscle brace or a mouth trainer and is therefore actually a 'gym' for your mouth.
The Myobrace helps to correct abnormal oral habits. The dental arch is also widened by the light pressure on the teeth. The appliance must be worn for at least 1 hour each day , night and day. In addition, your child must do a number of exercises each day to train breathing, tongue and lips.
The average duration of treatment is 1-1.5 years, but varies depending on the child's development, type and severity of the abnormality, age and cooperation of both the child and the parents.
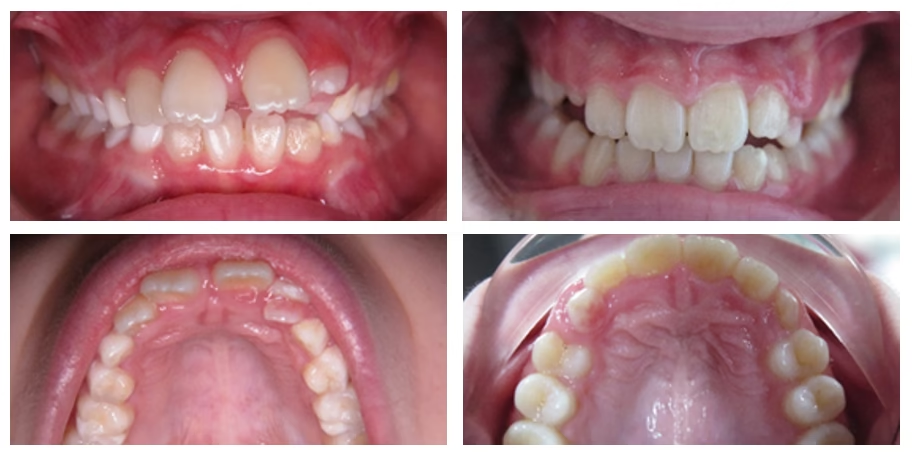
When to start
- Thumb sucking, finger sucking, pacifier sucking, etc. that is difficult to stop;
- Mouth breathing and/or open mouth behavior;
- If there is 'loose' lip tension;
- If there is a narrow and / or high palate;
- In case of speech difficulties, e.g. lisping or slurring;
- In case of difficulties with swallowing or eating;
- If there is an incorrect tongue position at rest or during swallowing;
- For jaw joint complaints;
- In case of grinding behavior;
- If the 'corrected' abnormality returns (partially) after orthodontic or jaw-correcting treatment.